6. Rover Web UI: roverweb¶

6.1. What is roverweb?¶
roverweb is a Web-based user interface that includes not only powerful back-end communication infrastructure with roverapp, but also provides functionalities such as driving the rover, camera streaming, visualizing core utilization, displaying sensor information, and sensor calibration.
Roverweb is equipped with a powerful embedded back-end that is called node.js and a main infrastructure library called socket.io. It makes use of the created javascript programs in order to create reactive web servers that communicate with websockets.
6.3. roverweb Features¶
6.4. Downloading roverweb¶
Note
Rover-web source code is maintained under the following repositories:
6.5. Getting started with roverweb¶
6.5.1. Installation¶
Note
In order to see how roverapp is installed and compiled, please see roverweb Installation section.
6.5.2. Running the Application¶
Before running the application, make sure that installation steps are successfully completed. In order to run the server after installation, the following command must be executed from roverweb root:
1 2 | cd <your/roverweb/root/path>/scripts/nodejs/
sudo node start_roverweb.js
|
Warning
Be sure to change the folder to cd <your/roverweb/root/path>/scripts/nodejs/ before executing the script, since it’ll use default directory for hosting.
After reading from the console that HTTP server is running, the web interface could be accessed using http://192.168.168.1:5500/roverweb.html.
Before the web interface can be opened, it is important for one to connect to the network (using SSID/PSK) of the rover.
For roverweb’s operation, it is not necessary for roverapp to be running. However, full functions of roverweb could be benefited when roverapp is also running.
6.5.3. Starting the Camera Stream¶
After mjpg_streamer is installed, one can start the camera stream in roverweb using the following command:
1 2 | cd <your/roverweb/root/path>/
sudo bash scripts/bash/camera_stream/start_camera_stream.sh
|
Warning
Be sure that the start_camera_stream.sh is given execution permissions. This is achieved by sudo chmod +x scripts/bash/camera_stream/start_camera_stream.sh.
6.6. roverweb Complete Reference¶
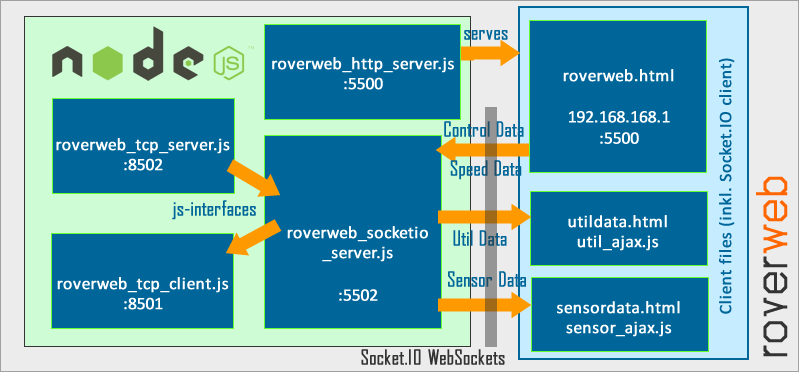
6.6.1. Some Words on Infrastructure¶
Roverweb consists of the following elements:
roverweb_http_server.js: HTTP server realizes web interface contents in a proper fashion. Thus, the information can be displayed using web browsers.roverweb_tcp_client.js: Reactive TCP client that connects to the TCP client end port and sends information to roverapp. TCP client implementation uses NET sockets and is implemented in a manner that constantly tries to reconnect if a connection fails.roverweb_tcp_server.js: Reactive TCP server that connects to the TCP server end port and receives information from roverapp. TCP server implementation uses NET sockets and is implemented in a manner that constantly tries to reconnect if a connection fails.roverweb_socketio_server.js: SocketIO server is a core implementation that handles Websocket communication betweenroverweb_socketio_server.jsandroverweb_tcp_server.jsandroverweb_tcp_client.jsusing HTTP protocol. It is able to pass data to/from HTTP server.js-interfaces: Interface files are responsible for variable globalisation betweenroverweb_socketio_server.jsandroverweb_tcp_server.jsandroverweb_tcp_client.js.
Once the application is run using start_roverweb.js each of these components are initiated, and the web interface is available at http://192.168.168.1:5500/roverweb.html.
6.6.2. Ports¶
roverweb uses several ports in the network stack in order to keep communication running. The allocated ports are given below:
HTTP server: 5500
Socket.IO server: 5500 (same port as the HTTP)
Roverweb TCP server end: 8502
Roverweb TCP client end: 8501
6.6.3. Data Formats¶
Four types of data is currently passed between roverapp and roverweb’s reactive socket processes. Those data are all JSON formatted, concatenated with
end of file (EOF) string \r\n.
Sensor Data (from roverapp to roverweb), denoted by
sensorCore Utilization Data (from roverapp to roverweb), denoted by
utilRover Control Data (from roverweb to roverapp), denoted by
controlRover Speed Data (from roverweb to roverapp), denoted by
speed
Example data are shown below for each of the given data format types:
- Sensor Data
Data is periodically sent from roverapp to roverweb.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
{ "rover_dtype" : "sensor", "data" : { "infrared0" : 100.0, "infrared1" : 100.0, "infrared2" : 100.0, "infrared3" : 100.0, "front" : 20, "rear" : 15, "temperature" : 22.0, "humidity" : 67.0, "bearing" : 47.0 } }\r\n
- Utilization Data
Data is periodically sent from roverapp to roverweb.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
{ "rover_dtype" : "util", "data" : { "core0" : 100.0, "core1" : 100.0, "core2" : 100.0, "core3" : 100.0, } }\r\n
- Control Data
Data is asynchronously (upon user events) sent from roverweb to roverapp.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
{ "rover_dtype" : "control", "data" : { "command" : "F", } }\r\n
commandentry can indicate many integrated functions, such as the ones listed below:P → Parking Mode Left
O → Parking Mode Right
U → Compass Calibration
M → Adaptive Cruise Control Mode
X → Manual Drive Mode
L → Booth Mode - Demo1
N → Booth Mode - Demo2
R → Shutdown Hook
U → Compass Calibration
F → Stop Movement
Q → Go Forward-Left
W → Go Forward
E → Go Forward-Right
A → Go Backward-Left
S → Go Backward
D → Go Backward-Right
J → Turn Left On Spot
K → Turn Right On Spot
- Speed Data
Data is asynchronously (upon user events) sent from roverweb to roverapp.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
{ "rover_dtype" : "speed", "data" : { "speed" : 360, } }\r\n